

References to non-updatable views in the FROM clause.Subqueries in the SELECT or WHERE clause referring to the table appearing in the FROM clause.Multiple references to any column of the base table.Such clauses as GROUP BY, DISTINCT, HAVING, UNION or UNION ALL.However, please note that in order to be updatable, your view must not include any of the following:
#Mysql create view examples update#
If you need to update tables through views, you can use the INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements to perform the corresponding operations with the rows of the underlying table. For that purpose, we calculate the total income using the order_details table data and use the INNER JOIN clause to retrieve order IDs from the orders table and customer names from the customers table. This view gives us information on order income per customer, grouped by order ID. INNER JOIN customers USING (customer_name) SUM(ordered_quantity * product_price) total Our next example is somewhat more complicated since it involves multiple tables (there will be three in our case): CREATE VIEW order_incomes AS
#Mysql create view examples how to#
How to create a view with JOINs to combine data from multiple tables The output will constitute a table containing three columns: id_number, name, and transaction_date. Now we can move on and execute a statement that selects all the fields in this view: SELECT * FROM transactions If we have a table called customers in our current database, and we would like to request a list of customers with the transaction dates of their orders, the script may look as follows: CREATE VIEW transactions ASĪfter we execute this statement, the transactions object will be available in Views. select-statement is a specified SELECT statement that can query data from tables or views.defines the required list of columns that can be indicated in parentheses after the view name by default, the list of columns is retrieved from the select list of the SELECT statement.view_name is a unique name of the view you are creating.is the name of the database where your view will be created if not specified, the view will be created in the current database.The basic syntax for creating a view in MySQL is as follows: CREATE VIEW view_name How to create a simple MySQL view with the CREATE VIEW statement How to create a view in dbForge Studio for MySQL.How to create a view with JOINs to combine data from multiple tables.How to create a simple MySQL view with the CREATE VIEW statement.
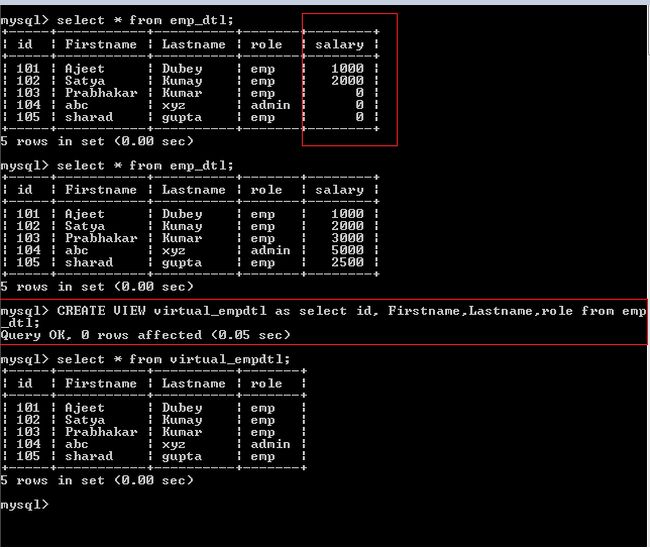
Essentially, a view is a result of SQL query execution, which returns the required rows of data from one or multiple tables. A view is a virtual table that does not store its own data but rather displays data that is stored in other tables. Let’s take some examples of using the create view statement.This article will show you how to create and manage views in MySQL. In case you want to use different column names, you can explicitly specify them in parentheses after the view name. The view uses the select list of the select statement for its column names. Finally, specify a select statement following the as keyword.Note that you cannot use the if not exists and or replace clauses at the same time. Third, specify the if not exists clause to conditionally create a view only if the view does not exist.Second, use the or replace clause if you want to overwrite an existing view if the view that you are creating already exists.First, specify the name of the view that you want to create after the create view keywords.View view_nameĬode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
